Dial Plan Intro
Up until now, the main sections of the PBX for the initial setup of the Call Center have been introduced. In this section, we will take a general look at one of the most important parts of the system, the Dial Plan editor. We will also review how to work with the dial plan and how to use its components.
Call Scenario
Businesses consider different call scenarios for their customers. For example, in many businesses, customer feedback is very important, and it is expected that before the call ends, the system will automatically conduct a Poll to assess the operator's performance. In some businesses, answering calls is crucial, and the user expects that if someone calls their extension and they are unable to answer, the call will be forwarded to their mobile number (Follow Me). In certain organizations, restricting the access level for outgoing calls (Outgoing Route) is essential for users (such as internal-to-internal, local, national, or international calls). There are many other scenarios that your organization may consider. To implement these scenarios, we use the Dial Plan.
Dial Plan
Implementing a call scenario with all its features in traditional VoIP systems is a complex and time-consuming task, and in some cases, it requires dial plan programming. Therefore, the goal of Simotel's Call Center is to implement a dial plan that is simple and user-friendly. In this dial plan, the user does not need to engage in coding and can easily understand the main elements of this section and implement their desired scenario.
Click on the image to view the implemented call scenario in the dial plan.
If you do not have access to the Call Center, visit here to test the dial plan features.
Dial Plan Components
sheets
The dial plan is designed in a way that allows you to create different pages, breaking down your scenario into smaller sections, and implementing each section on a separate page. This feature is useful when your call scenario becomes complex. For example, when using the bulk call module, it's better to design the scenario for bulk calls on a dedicated page and then connect it to the main scenario using the Jump In & Jump Out connector components.
By default, the dial plan includes two pages, and we will examine the purpose of each one.
-
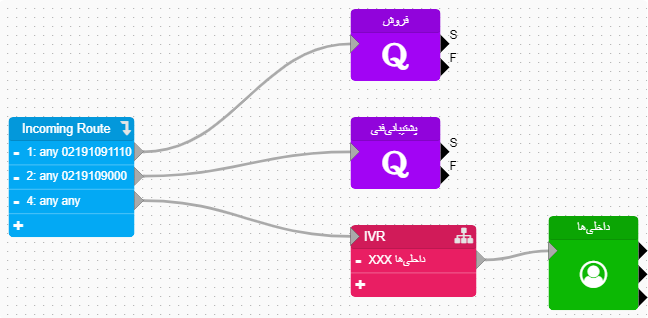
sheet incoming:All incoming calls to the system (when a user's extension starts ringing) are managed on this page. To set working hours restrictions, route calls to a queue, add voicemail, conduct surveys, or receive faxes, changes should be made on this page.
-
sheet outgoing: All outgoing calls from the system (when a user picks up the phone and starts dialing) are managed on this page. To apply restrictions on outgoing calls, create conference rooms, monitor calls, reserve calls, or use the PickUp feature, changes should be made on this page.
components
Components are elements placed on the page that, through the wiring and connection between them, build the call scenario. Each component has a specific function and covers one of the features of the Call Center. For example, all incoming calls start with the Incoming Route component, and from there, they are distributed within the dial plan.
Call routing in the dial plan is defined using wiring. By connecting the output of one component to the input of another, the call path is determined. To do this, simply click on the output of a component, a wire will appear, and then connect the end of the wire to the input of the next component.
To use the components, there is a tab called Components at the top right of the dial plan page. By clicking on it, a list of available components will be displayed. To view all the components, you should use the mouse scroll. Finally, you can drag and drop the components onto the page to place them.
Features of Components
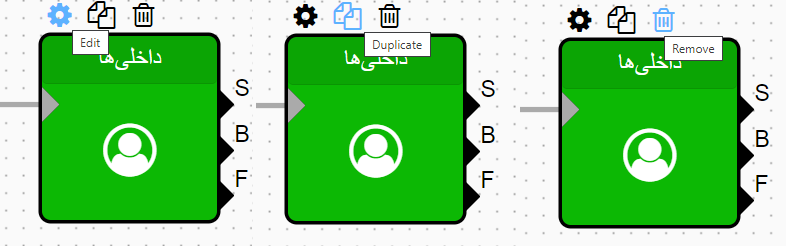
All components share common features that can be accessed by clicking on them:
-
Edit: Each component has specific settings based on its function. When you click on a component, a gear icon appears at the top, which provides access to its settings.
-
Duplicate: Often, you may need to use a component multiple times on the page. The Duplicate option allows you to create a copy of the existing component.
-
Remove: This option is used to remove a component from the dial plan.
Commonly Used Components
Incoming Route
This component is responsible for managing all incoming calls to the system. In other words, all incoming calls in the dial plan start with this component. Therefore, every call scenario must include an Incoming Route component to manage incoming calls. One of the key features of the Incoming Route is the Context, which determines the access level and must match the Context in the defined trunks. In this component, based on the priority of the source and destination numbers, it is possible to route the call to different paths, which will be explained further.
If there is no change in the default Context value of the defined trunks, this value will be the same as the Context in the Incoming Route.
Outgoinig Route
The Outgoing Route component is responsible for managing outgoing calls in the Call Center. Any call originating from the Call Center enters this component first, and then, based on the designed scenario, it is routed to the specified path. This component is used on the Outgoing page, and since the Outgoing Route is the origin for outgoing calls, it is essential to have an Outgoing Route component in the outgoing page.
In the Outgoing Route, you can use the Match Pattern to route calls to different destinations. A professional use of the Outgoing Route requires an understanding of pattern matching, which will be covered in detail later.
One of the main features of the Outgoing Route is the Context value, which allows you to control the access level (internal-to-internal, local, national, international) for extensions. This helps in limiting the types of calls that internal users can make.
If the default Context value for the defined extensions is not modified, this value will be the same as the Context in the Outgoing Route.
Exten
The purpose of this component is to connect calls to extensions. Wherever a call needs to be connected to an extension in the dial plan, the Exten component is used. There are two scenarios for using this component:
-
When it is clear which extension the call should be connected to, and the call is directly routed to that extension.
-
When there is a range of extensions, and the caller is supposed to enter the specific extension number they want to reach, such as in an interactive voice response (IVR).
In the Edit section of the component, there is a parameter called Extension. If a specific extension number is selected, the first scenario is implemented, and the call is directed to that extension. However, if no specific extension is selected and this parameter is left empty, any extension number entered by the caller in the IVR will be considered as the target extension, triggering the second scenario.
Queue
The purpose of this component is to route calls to a queue. To use it, in the Edit section of the component, set the Queue parameter to the name of the queue created under the PBX > Queues section. After that, calls will be directed to the selected queue.
Announcement
If an audio file needs to be played for the user, this component is used. To select the audio file, in the Edit section of the component, set the Announcement parameter to the name of the uploaded audio file.
Make sure to use the Answer component before any Announcement component, and connect the output of the Answer component to the Announcement component.
IVR
This component is used to set up an Interactive Voice Response (IVR). To upload an audio file, click on the Edit section of the component and set the Announcement parameter to the name of the uploaded audio file.
In an IVR, the case feature is used to route calls to different destinations. To add a new case in the IVR, use the ➕ option in the component.
-
Defining a case:
When an audio message is played, based on the uploaded audio file, a set of options is provided to the caller, such as "Press 1 to connect to Sales." The system needs to know what action to take when the caller presses a specific number, and how the call should be routed afterward. This process is called defining a Case in the IVR. -
Important: Always use an Answer component before any IVR component.
Time Condition
This component is used to check time-based conditions.
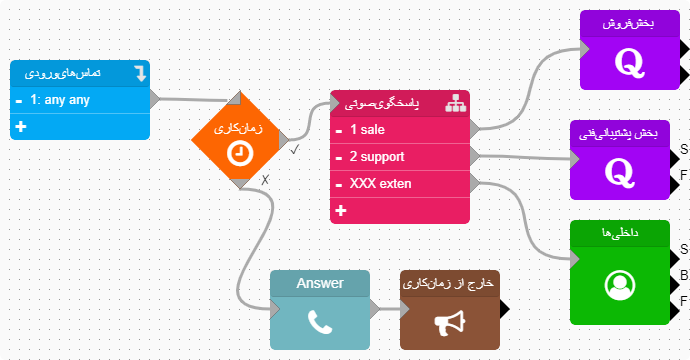
Example: A person calls the company.
-
If the working hours and days of the week conditions are met, the call will proceed along the ✔️ path and be routed to the IVR (Interactive Voice Response).
-
If the working hours or days of the week conditions are not met, the call will exit through the ❌ path and finally inform the caller that they are calling outside of business hours.
To set time-based restrictions, click on Edit in the component. By clicking on the ➕ sign in the days of the week section, you can specify your working hours.
Further details of the dial plan are covered in the relevant section.